We would like you to be as informed as possible about the services, procedures, insurance, billing, and more. If there is a question we can address for you, please reach out to us, and we will do our best to provide that information promptly.
We understand the significance that your exam may have for you and we recognize the value of having someone close to you present during your scan. We allow 2 guests in the exam room during your sonogram. If you wish to bring a young child, please bring an adult that can supervise the child if necessary.
Whenever possible, we will provide you with paper prints and/or digital images as well as video sent directly to your smartphone so you can easily share them with your loved ones. This is a complimentary service provided to you just for choosing us.
Read More →
An ultrasound examination does not guarantee a normal baby. Many kinds of abnormalities can be seen with ultrasound; however, our ability to detect any abnormality depends on how well we can see. The quality of the ultrasound image directly affects our ability to detect an abnormalities.
Occasionally, it is necessary to have a patient return to re-evaluate a structure that was sub optimally visualized.
The American Institute of Ultrasound in Medicine has issued the following statement:
"There are no known harmful effects associated with the medical use of sonography. Widespread use of diagnostic ultrasound for many years has not revealed any harmful effects. Studies in humans show no direct link between the use of diagnostic ultrasound and any adverse outcome. Although the possibility exists that biological effects may be identified in the future, current information indicates that the benefits for patients far outweigh the risks, if any."
Proper exam preparation is important because it helps to eliminate factors that hinder our ability to see with ultrasound. A full bladder serves as a window to better see the uterus during GYN and obstetric scans. A full bladder is also needed for a kidney scan because measurements of the bladder volume are obtained before and after urination to assess the bladders ability to empty. Refraining from eating or drinking for 8 hours before an abdominal scan allows the gallbladder to remain distended so that it can be evaluated for the presence of stones. It also helps eliminate excessive bowel gas, which hinders visualization of other abdominal organs. Prepare For Your Exam →
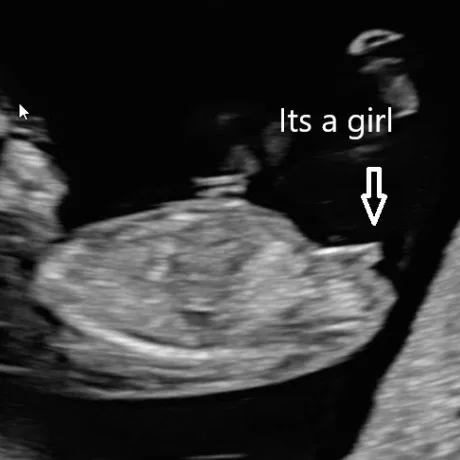
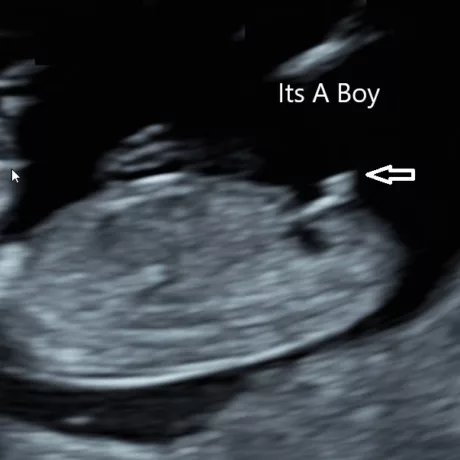
A baby's sex can be determined as early as week 12. However, it is not as accurate until weeks 18-20 at your anatomy scan.
At 12 weeks, male and female fetuses have a bump called a genital tubercle. The bump represents the developing genitalia. During this stage of development, the genital tubercle begins to point either toward the head, which means boy, or toward the feet, which means girl.
As much as we hope your little one will cooperate, they may have other plans. Crossed legs, the presence of the umbilical cord between the legs, or other less-than-ideal fetal positions can prevent the sonographer from getting a good look.
Yes. If you have a preference for a particular sonographer to perform your exam, you may make a request at the time of scheduling. We will try our best to coordinate your appointment with our staff schedule; however, this may not always be possible.
In most circumstances, vaginal bleeding does not interfere with the exam.
In emergent cases, or if requested by your referring provider, a preliminary report of findings will be provided immediately following the examination. Final reports are typically available in the morning of the next business day.
Keepsake Video